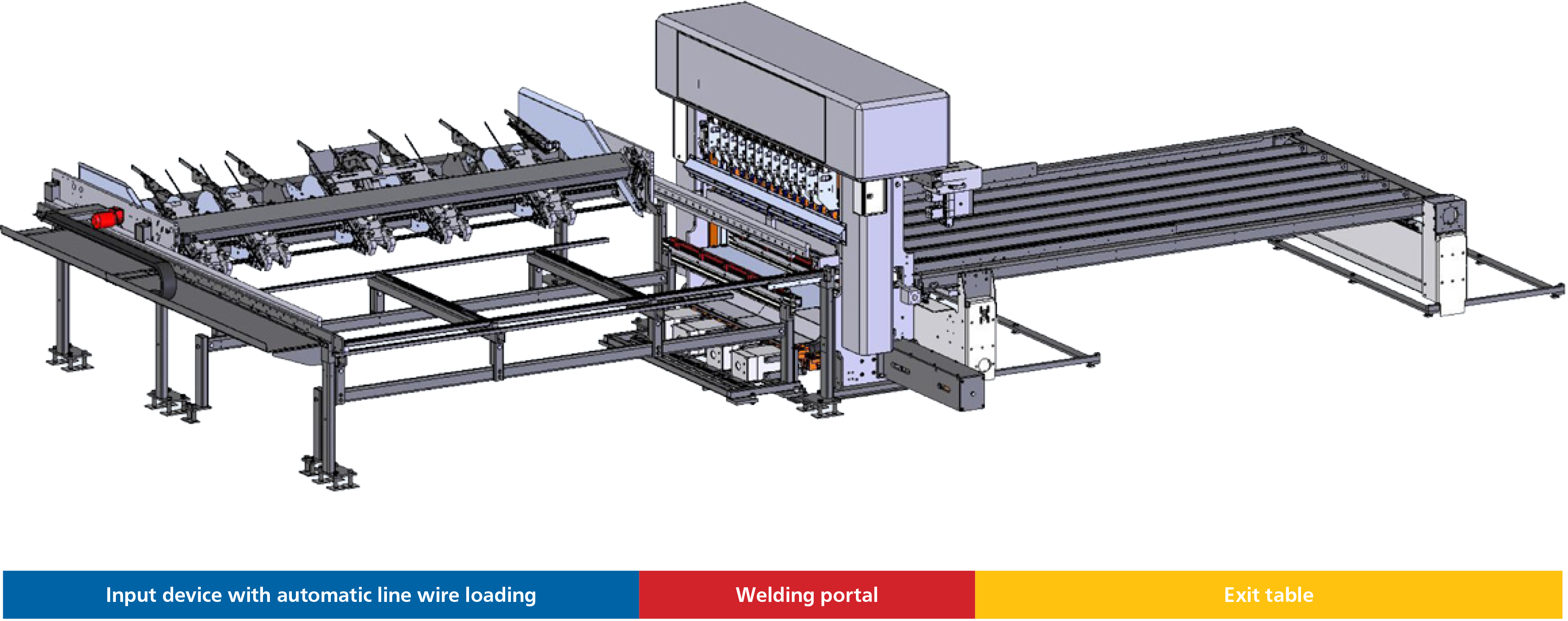
Type GA mesh welding machines
The machine solution for the unrestricted production of all product variants and material combinations of wire grids and fences with various wire diameters and lengths, including mesh frame combinations.
IDEAL mesh welding machines are in widespread use in the wire goods industry.
Leading manufacturers of wire goods rely on IDEAL machines in order to be able to fabricate the base grids for their products in a flexible and economical manner. When required, IDEAL automatic production lines perform additional processes such as punching, embossing, bending, etc. on the product, ensuring that a finished product is achieved at the end of the line. They are, for example, ideally suited for the production of fences and industrial mesh in single or double wire for 2D, 3D, 358, grates or machine protective grating as well as for the production of cable trays or mesh floors. Subsequently, only the finish / surface coating has to be performed.
Manufacturing Line for Cable Tray
Process all product variants and material combinations
Experience the speed of the new GA 800 series.
- Up to 200 strokes per minute (depending on the pitch and wire Ø)
- Quick and tool free change over possibilities for minimized down time
- New designed welding cylinders (adjustable 3,5 kN / 7 kN)
- 1, 2 or even more secondary circuits in medium frequency DC technology for the combination of different input materials
Down to the smallest detail: Type GA mesh welding machine.
Taking a closer look at the details of the type GA mesh welding machines is worth your while. Here you can see the technical details, the typical functional ranges and more detailed information on the technology behind the GA mesh welding machines. You will learn why IDEAL utilises modular mechanical engineering in order to fulfil your requirements and expectations.
The modules of the mesh welding machine GA
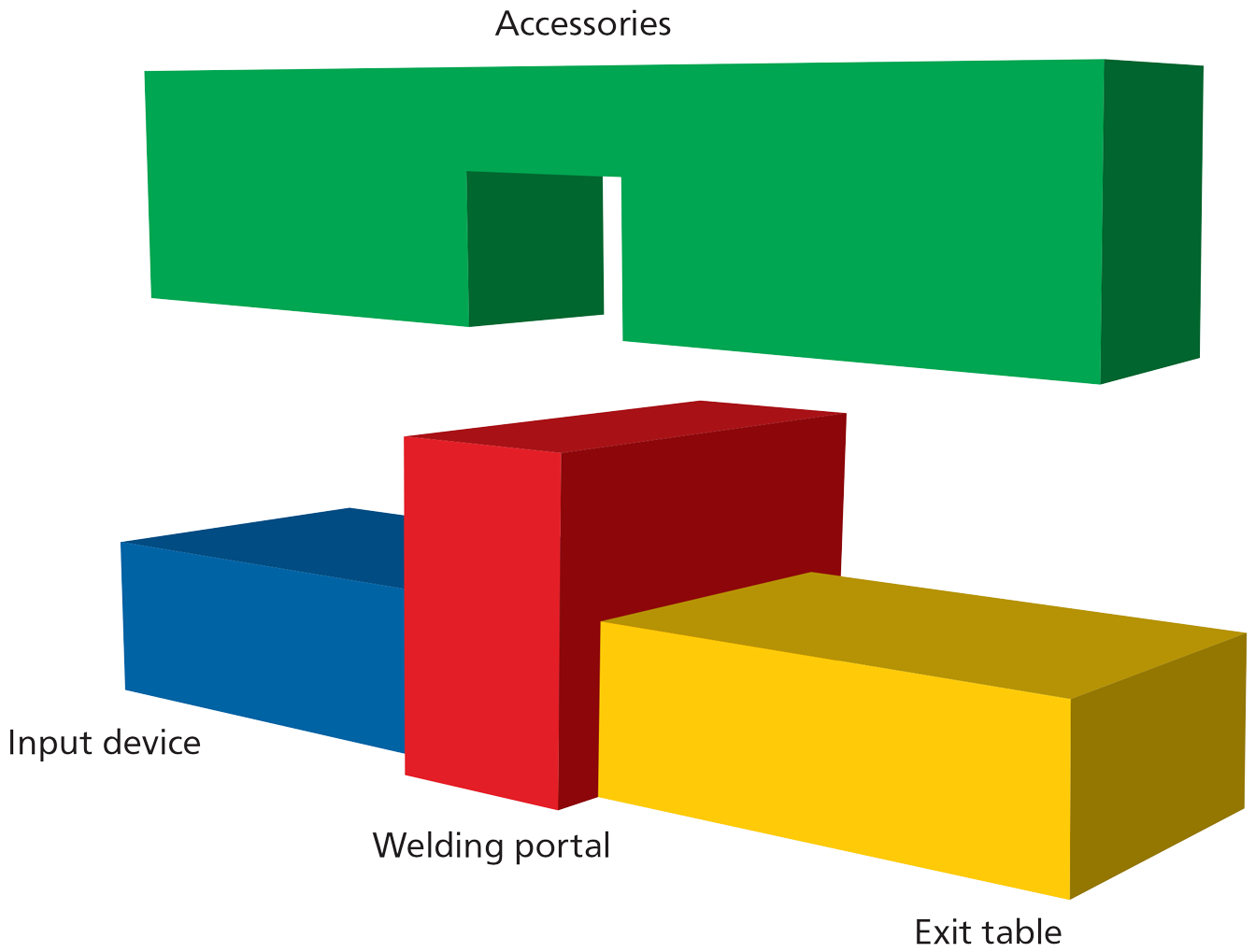
The welding portal forms the centre of the mesh welding machine. For a completed wire product to be created, the loose wires, flat bars and frames must be supplied to the welding portal and the welded products must be transported out of the welding portal.
Subsequently, additional fabrication steps such as punching, embossing, bending, etc. can be arranged in an automated production line, in order to achieve a completed product at the end.